Indus River System (सिंधु नदी प्रणाली): Importance for India and Pakistan जानिए यहाँ
Indus River System, South Asia का सबसे important और historical river network है, जो agriculture, irrigation, और hydropower में critical role निभाता है। आइए इस blog में Indus की origin से लेकर इसके tributaries, benefits, major projects और environmental issues को detail में समझते हैं।
Indus River Origin: कहाँ से निकलती है सिंधु नदी?
Indus River या Sindhu River की शुरुआत Tibet के Kailash Range में glaciers से होती है।
- Tibet से निकलकर ये Ladakh और Gilgit-Baltistan से होकर Pakistan में प्रवेश करती है।
- करीब 3,180 km लंबा सफर तय करने के बाद Arabian Sea में समा जाती है।
Major Tributaries of Indus River System:-
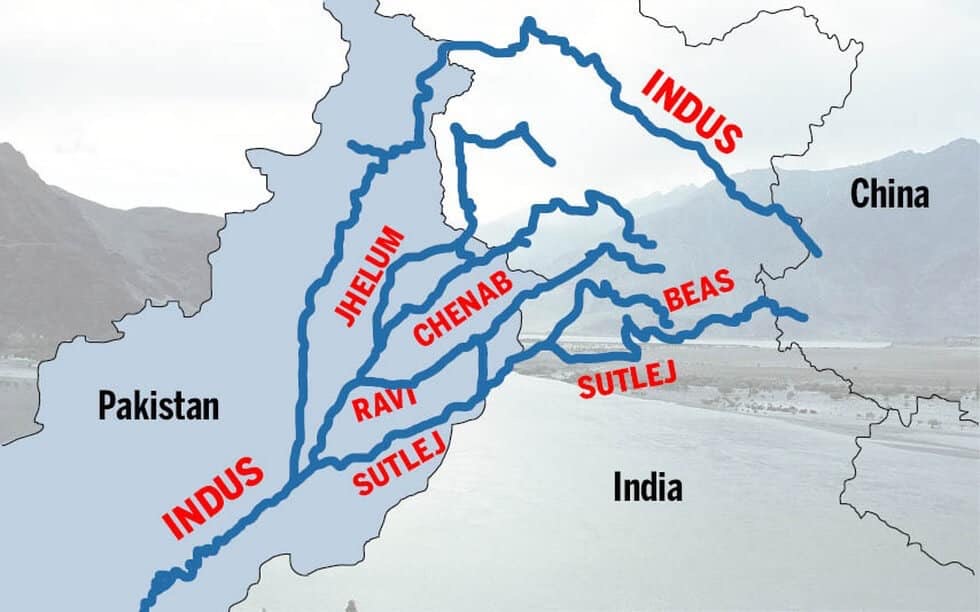
Left Bank Tributaries (हिमालय से):
- Jhelum River – Pir Panjal से निकलती है।
- Chenab River – Chandra और Bhaga rivers के confluence से बनती है।
- Ravi River – Kangra Valley, Himachal Pradesh से originate होती है।
- Beas River – Beas Kund से निकलती है।
- Sutlej River – Tibet से निकलकर हिमाचल होते हुए Indus से मिलती है।
ये पाँचों मिलकर Punjab Rivers कहलाती हैं।
Right Bank Tributaries (Hindu Kush और Karakoram से):
- Shyok River
- Gilgit River
- Kabul River (Afghanistan से)
- Kurram River
- Gomal River
Importance: India और Pakistan के लिए क्यों है ज़रूरी?
India में Indus River System के फायदे:
- Agricultural Irrigation: Punjab, Haryana, Rajasthan की खेती इस पर depend करती है।
- Hydroelectric Power Generation: कई बड़े dams जैसे Bhakra Nangal और Pong Dam बिजली पैदा करते हैं।
- Drinking Water Supply: Millions लोगों का water source।
Pakistan में Indus River का महत्व:
- World’s Largest Irrigation System: Indus Basin Irrigation System।
- Major Hydropower Projects: Tarbela और Mangla Dams।
- Fisheries और Transportation Support: Traditional livelihood का हिस्सा।
Major Dams और Irrigation Projects:-
India में:
- Bhakra Nangal Dam (Sutlej River)
- Pong Dam (Beas River)
- Thein Dam (Ravi River)
- Indira Gandhi Canal (Rajasthan के desert areas के लिए)
Pakistan में:
- Tarbela Dam (Indus River)
- Mangla Dam (Jhelum River)
- Ghazi-Barotha Hydropower Project (Indus River)
Agriculture पर Deep Impact:-
- Highly Fertile Plains: Punjab और Sindh की धरती दुनिया की सबसे productive agricultural lands में गिनी जाती है।
- Multi-Crop Cycles Possible: Thanks to year-round irrigation.
- Economic Growth Driver: लाखों farmers और rural communities की backbone।
Environmental Challenges Facing Indus River:-
- Water Scarcity: Population boom और climate change की वजह से।
- River Pollution: Industrial और agricultural waste की वजह से पानी की quality गिर रही है।
- Soil Salinity और Waterlogging: Over-irrigation का side effect।
- Glacier Melting: Global warming से Indus का long-term water flow खतरे में।
Indus Waters Treaty (1960): India-Pakistan Water Sharing Agreement
- Eastern Rivers (Ravi, Beas, Sutlej) इंडिया के पास।
- Western Rivers (Indus, Jhelum, Chenab) पाकिस्तान के पास।
- World Bank ने इस treaty को broker किया था।
- आज भी ये treaty regional peace के लिए key है, despite occasional tensions.
Conclusion: Future of Indus River System:-
Indus River System सिर्फ एक नदी नहीं, बल्कि South Asia की आर्थिक, सामाजिक और agricultural life की धड़कन है। लेकिन sustainable management, climate change adaptation और India-Pakistan cooperation के बिना इसका future secure नहीं होगा।
Understanding और sustainable use ही Indus River System को आने वाली generations के लिए बचा सकता है।

